Moving equipment in early childhood education and care
This guide helps manage the risk to workers in the children’s services sector of musculoskeletal injuries from manually moving or carrying equipment.
Download this fact sheet (PDF, 286.79 KB)
What is the problem?
Workers in the children’s services sector experience musculoskeletal injuries (for example, sprains, strains, fractures and soft tissue injuries) from manually moving or carrying equipment.
Equipment includes large, bulky, awkward or heavy objects such as indoor and outdoor play equipment (eg climbing frames, model kitchens, bookcases or block trolleys). Equipment also includes objects such as evacuation cots and children’s furniture.
Equipment is frequently moved in children’s services to provide children with a stimulating or changing environment. Organisations are encouraged to discuss how equipment is moved so the needs of workers and children are addressed safely.
What are the risks?
Workers may be at risk of injuries from:
- Bending, twisting and exerting high or unexpected force due to manually lifting, moving or carrying heavy or awkward indoor and outdoor equipment.
- No aids being available to move equipment (eg trolleys).
- An insufficient number of people to undertake the task.
- Pushing or pulling evacuation cots that are difficult to manoeuvre over uneven surfaces or in small spaces.
What are solutions to the problems?
Systems
Develop systems of work that:
- Where possible, reduces or eliminates equipment having to be packed or stored away.
- Considers the weight, size and manoeuvrability when purchasing or replacing equipment.
- Identify and label the weight, size and handling instructions for equipment that is moved (eg whether equipment must be moved with an appropriate aid such as wheels or a trolley or if it can only be moved with two people).
- If facilities are shared with other organisations, designate how equipment should be moved, who will move equipment and when it will be moved.
- Provides workers with information, instruction and supervision on documented work procedures and use of equipment and aids.
- Provides reporting processes so safety issues can be identified and fixed as soon as possible.
- Schedule and record regular inspections and maintenance of all areas of the workplace and equipment.
Equipment
- Replace heavy or awkward equipment with lighter equipment.
- Replace heavy or awkward equipment with equipment with lockable wheels, so it can be easily moved.
- Store equipment close to where it is used.
- Use trolleys for moving heavy or awkward objects rather than manually lifting and carrying objects such as when moving multiple objects, chairs, tables etc.
For example:
- match the trolley to the weight and dimensions of the objects that are being moved
- designate appropriate routes for trolleys so they are not pushed over surfaces with a high level of friction or resistance or lifted over structures such as steps.
- When moving stretcher beds, ensure they are transported using a wheeled platform and the platform is moved using a handle to eliminate awkward postures when beds are unstacked.
- Use sandpit covers that are segmented or rolled to reduce manually lifting the entire cover.
- Store objects in smaller rather than larger containers to avoid having to lift and balance heavy loads.
- Use lightweight, sturdy, stackable containers with wheels and handles to store or move objects.
Evacuation cots
- Measure doorways to ensure they are wide enough for evacuation cots.
- Fit evacuation cots with large diameter wheels (eg 100-150mm) to assist with the negotiation of external surface obstacles. Wheels should be sturdy, lockable and well maintained to move the cot with minimal resistance.
- Assess the floor and ground surfaces of the evacuation route for minimal friction (eg no thick carpet, tanbark or broken concrete), and modify existing surfaces where necessary.
- Remove or modify any structures the evacuation cot needs to be lifted over (eg steps or raised door frames).
- Ensure emergency exits are accessible at all times and are not locked or blocked.
The problem
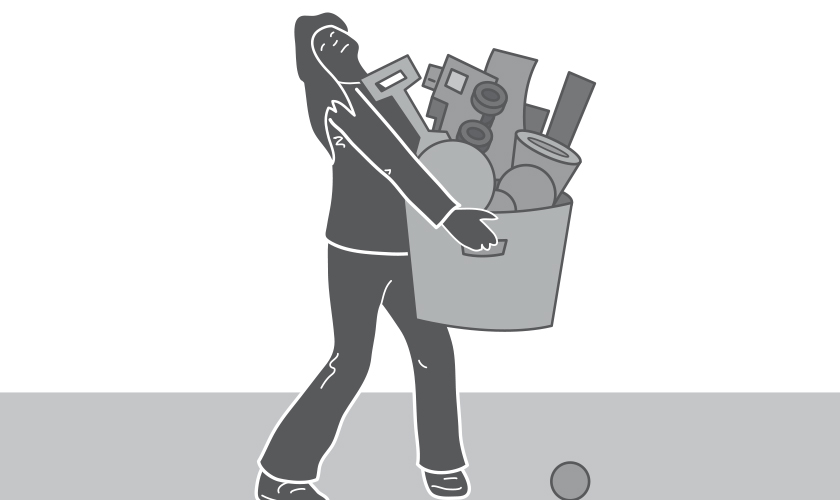

Worker is at risk of injury when manually lifting and carrying heavy or awkward objects.
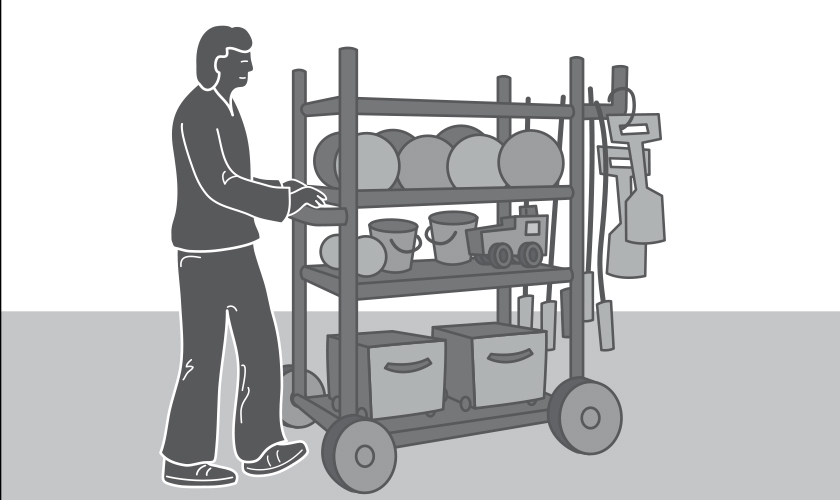
A solution
Trolley used to move playground equipment and toys, reducing the need to manually lift and carry objects. Large wheels help move the trolley over uneven surfaces.
Further information
SafeWork NSW resources
- Using cots, highchairs and change tables in early childhood education and care
- Working at low levels in early childhood education and care
- Storing supplies and equipment in early childhood education and care
- Conducting administrative tasks in early childhood education and care
- Maintaining indoor and outdoor areas in early childhood education and care
SafeWork NSW publications
- Hazardous manual tasks, code of practice (PDF, 1499.23 KB)
- Hazardous manual tasks
- Hazardous manual tasks overview fact sheet (PDF, 8034.42 KB)
- Healthcare and social assistance
Australian Standards
- AS/NZS 4422:2016, Playground surfacing – specifications, requirements and test method
- AS/NZS 4685.1-2014
General notice
The information is intended for general use only. Every effort has been made to ensure the information is complete and accurate. The advice contained may not apply in every circumstance. SafeWork NSW cannot be held responsible, and extends no warranties as to the suitability of the information for your specific circumstances; or actions taken by third parties as a result of information contained in this advice.
Copyright advice
This guidance material is WorkSafe Victoria copyright material which may not be reproduced or used without express written permission from WorkSafe Victoria. WorkSafe Victoria is not liable and does not take any responsibility whatsoever for, or for reliance on, information contained in this guidance material.